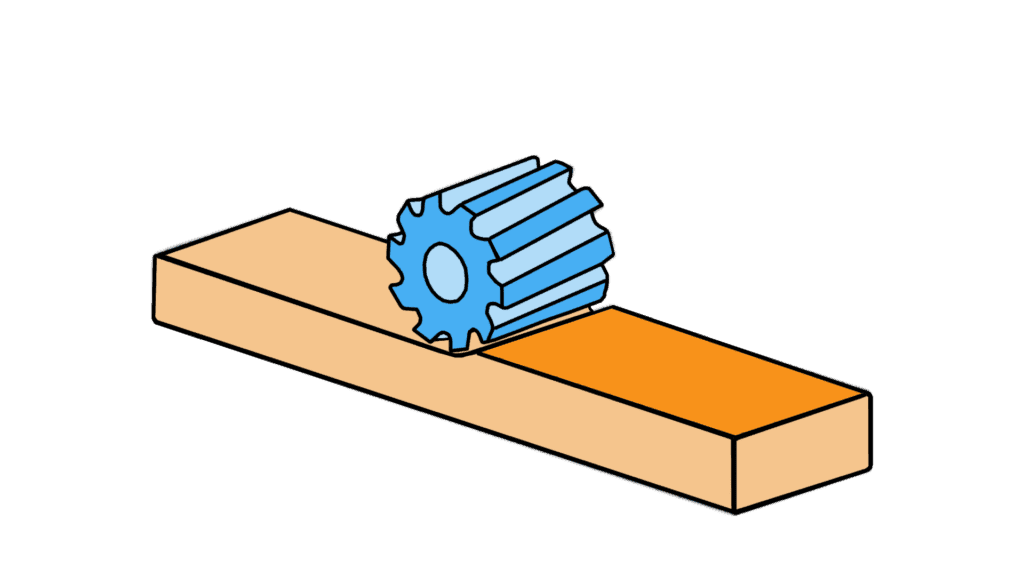
Have you ever wondered how flat surfaces are precisely machined on metal parts? One of the most common techniques is plain milling, a fundamental machining process with a wide range of applications.
Plain milling is a fundamental machining operation that forms the backbone of various manufacturing processes. This method is widely used in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace, where precision and surface finish are crucial. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of plain milling, covering its process, tools, advantages, applications, and more.
What Is Plain Milling?
Plain milling, also known as slab milling, is a machining process primarily focused on creating flat surfaces, grooves, and various features on a workpiece. This operation typically employs a cylindrical milling cutter that rotates about its axis, cutting into the material as the workpiece is fed against it. It is ideal for producing uniform surfaces and is essential for many manufacturing applications, including component preparation and assembly.
How Does The Plain Milling Process Work?
The plain milling process begins with securely mounting the workpiece on the machine table. This can involve clamping or using fixtures to ensure stability during cutting. Once the workpiece is positioned, the milling cutter is mounted onto the spindle of the milling machine, and the operator sets the appropriate spindle speed and feed rate based on the material being machined and the desired finish.
The workpiece is securely clamped onto a worktable, which then feeds the workpiece against the rotating milling cutter. The cutter’s teeth remove material in the form of chips, gradually shaping the workpiece to the desired dimensions and surface finish. Think of it like shaving wood with a plane, but on a much more precise and controlled scale.
Types Of Plain Milling Cutters
Just like you wouldn’t use the same knife for everything in the kitchen, different milling cutters are designed for specific tasks. Plain milling cutters can be broadly categorized into two main types:
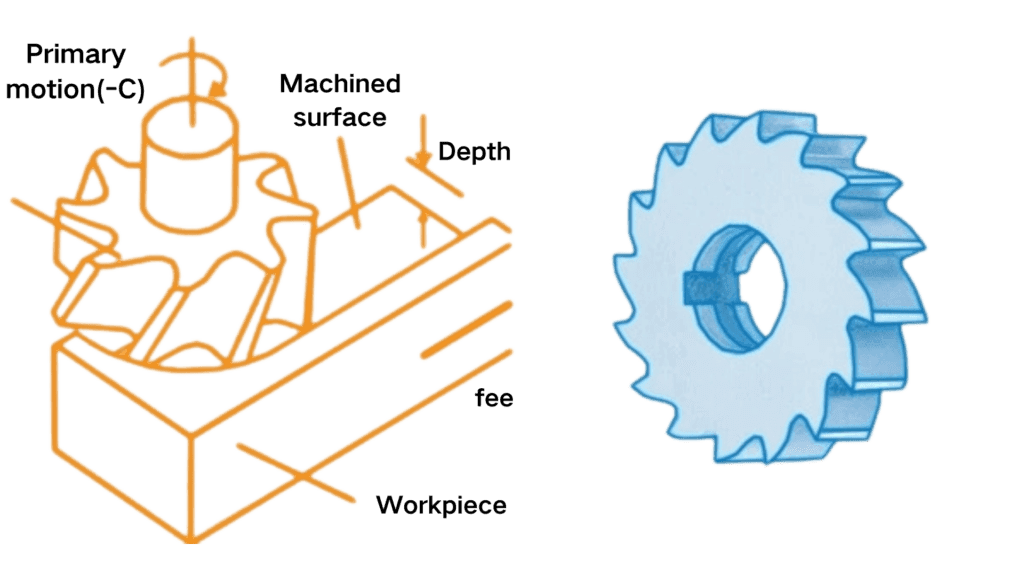
Light Duty Plain Milling Cutters
Light duty plain milling cutters are designed for less demanding machining tasks. These cutters are generally smaller in size and are suitable for applications that require precision without the need for heavy material removal. They are ideal for operations such as finishing, engraving, and milling softer materials. Their lightweight design allows for easier handling and quick setups, making them perfect for small-scale production and detailed work.
Heavy Duty Plain Milling Cutters
Heavy duty plain milling cutters are built for robust machining operations that require significant material removal. These cutters are larger, sturdier, and equipped with more teeth to withstand the stresses of high-speed cutting. They are suitable for roughing operations, machining hard materials, and producing large components. Heavy duty cutters are commonly used in industrial settings where efficiency and productivity are paramount. Their design allows them to remove material quickly while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Both types of plain milling cutters play crucial roles in various machining applications, ensuring that operators can select the right tool for the task at hand. Whether for intricate detail work or heavy-duty material removal, the appropriate plain milling cutter can significantly enhance machining efficiency and quality.
How To Choose Suitable Plain Milling Cutters?
Selecting the right plain milling tools is vital for achieving optimal machining performance and quality results. With various options available, understanding factors such as material compatibility, cutting depth, and operational requirements is essential.
Light duty plain milling cutters are designed for less demanding machining tasks. When selecting these cutters, material compatibility is a primary consideration. Light duty cutters are typically suited for softer materials or applications that do not require significant material removal, such as aluminum, plastics, and certain alloys. Additionally, cutting precision is crucial; if the machining demands high surface finish and tight tolerances, it is wise to choose light duty cutters that offer higher precision. Cutting depth is another important factor, as light duty cutters usually work best with shallower cuts. Therefore, assessing the required depth of cut is essential to ensure the right tool selection. Lastly, tooth count impacts the machining outcome, as cutters with more teeth can achieve smoother finishes, making them ideal for finishing and detailed work.
Heavy duty plain milling cutters are built for robust machining operations that require significant material removal. When selecting these cutters, material hardness is a key consideration. Heavy duty cutters are suitable for machining hard materials like high-strength steel and titanium alloys, so it’s important to ensure that the tools possess excellent wear resistance. If the primary application is rough machining, opting for heavy duty cutters with larger cutting depths and fewer teeth can improve material removal efficiency. The design of heavy duty cutters allows them to withstand greater cutting forces during high-speed operations, so it’s crucial to ensure that the machine tool can support the workload of the chosen cutter. Additionally, during rough machining, heavy duty cutters may require appropriate cooling and lubrication measures to prevent overheating and extend tool life.
By considering these factors, you can select the most suitable plain milling cutter based on your specific machining needs, ensuring both efficiency and quality in your operations.
Advantages Of Plain Milling
Plain milling offers several advantages that make it a go-to process for many applications. Its high efficiency, versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to achieve excellent surface quality are just a few of the reasons why it’s favored in various industries.

Plain milling is renowned for its high efficiency in material removal, making it suitable for both roughing and finishing operations. The design of plain milling cutters enables aggressive cutting, resulting in faster processing times and increased productivity. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in large-scale manufacturing, where time and output are critical. Additionally, plain milling tools are highly versatile, capable of machining various materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. This adaptability allows manufacturers to perform diverse tasks, including creating flat surfaces, grooves, and intricate shapes, making plain milling an invaluable tool in many industries.
Plain milling provides a cost-effective solution for machining needs. The simplicity of the process, combined with the durability of milling cutters, leads to lower tooling and operational costs over time. Furthermore, the ability to perform multiple machining operations with a single tool reduces the need for various specialized cutters, enhancing cost savings. One of the significant advantages of plain milling is the ability to achieve high surface quality. The precision of plain milling cutters allows for smooth finishes and tight tolerances, which are essential in many applications, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where the integrity of machined parts is crucial.
The plain milling process is relatively simple and easy to set up, making it accessible for operators of varying skill levels. The straightforward nature of the process minimizes the learning curve and allows for quick adjustments, enabling manufacturers to respond rapidly to changing production needs. This simplicity contributes significantly to overall operational efficiency and effectiveness, allowing businesses to maintain productivity while adapting to diverse machining requirements.
What Materials Are Suitable For Plain Milling?
This process is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Understanding the properties of different materials is essential for selecting the right tools and parameters, ensuring effective machining and desired outcomes.
Plain milling is commonly used for machining metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and various alloys. Each of these materials requires specific tools and cutting parameters to achieve optimal results. For instance, aluminum is favored for its lightweight and machinability, while steel and titanium demand robust tools due to their hardness and strength. Selecting the appropriate milling cutter and parameters ensures efficient material removal and surface quality for metal components.
Many types of plastics, including acrylic and polycarbonate, can be effectively machined using plain milling techniques. The ability to achieve smooth finishes and precise dimensions makes plain milling ideal for creating plastic parts in various applications, from consumer products to industrial components. The relatively low cutting forces required for plastics further enhance the efficiency of the milling process.
Advanced composites, particularly those used in aerospace applications, can also be processed efficiently with plain milling. These materials, often combining fibers and resins, require careful consideration of tooling and cutting parameters to prevent delamination and achieve the desired surface finish. The versatility of plain milling makes it an excellent choice for producing complex shapes and components in high-performance industries.
Plain Milling Tips
By following these tips, you can optimize plain milling for better efficiency and part quality.
- Minimize Vibration:Maintain appropriate clearance between the spindle and the cutting tool to reduce vibration during milling, enhancing stability and surface quality.
- Utilize CNC Technology:Use CNC machines to automate the process, improving accuracy and production efficiency while minimizing human error.
- Choose the Right Tooling:Select tool materials and cutting speeds based on the operation requirements. Carbide tools are ideal for high-speed milling, while carbon steel tools are suitable for low-speed applications.
- Implement Lubrication and Cooling:Use lubricants or coolants during milling to improve chip control, extend tool life, and enhance surface finish quality.
Application Of Plain Milling
This technique is widely used across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing. Its versatility allows it to produce flat surfaces, slots, and keyways, making it essential for many mechanical components.

Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, plain milling is commonly used to produce flat surfaces on engine components and chassis parts. This process ensures precise fitting and alignment of various components, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of vehicles. The ability to achieve high surface quality and dimensional accuracy makes plain milling a critical operation in automotive manufacturing.
Aerospace
Plain milling plays an essential role in the aerospace industry, where the creation of precision components is paramount. Parts must adhere to stringent specifications for dimensional accuracy and surface finish due to the high-stakes nature of aerospace applications. Plain milling techniques are employed to produce critical components, ensuring safety and performance in flight operations.
Machinery Manufacturing
In machinery manufacturing, plain milling is frequently employed in the production of machine bases, frames, and other structural components. The process allows for the efficient machining of large, flat surfaces and intricate shapes, which are essential for assembling robust and reliable machinery. The versatility of plain milling makes it a preferred choice for various manufacturing tasks in this sector.
General Fabrication
Plain milling is widely utilized in workshops for a variety of projects, ranging from custom parts to prototyping. Its adaptability allows fabricators to tackle diverse tasks efficiently, whether creating one-off components or producing small batches. The straightforward setup and operation of plain milling machines make them a staple in general fabrication environments.
Overall, the versatility and effectiveness of plain milling make it a valuable process across multiple industries, ensuring high-quality results in various applications.
Plain Milling Vs Other Milling Processes
When comparing plain milling with techniques like contour milling and face milling, you’ll find key distinctions in tool engagement, surface finish, and machining strategy. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right milling process for your specific needs.
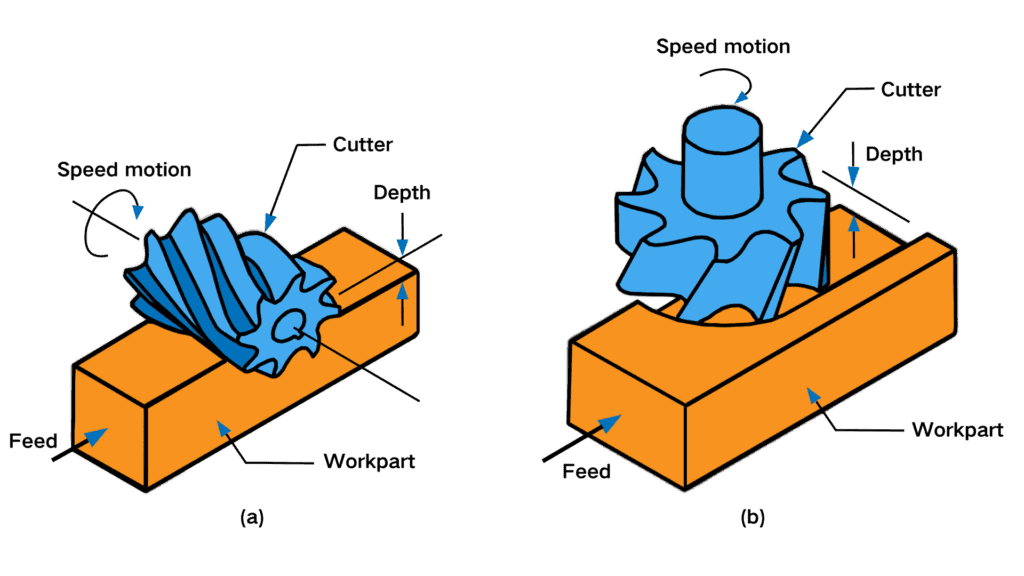
Plain milling primarily focuses on flat surfaces, making it simpler and more straightforward. In contrast, contour milling deals with complex surface geometries, allowing for more intricate designs. While plain milling is efficient for standard flat surfaces, it may lack the flexibility needed for handling complex shapes, which can limit its application in more detailed projects.
One of the advantages of plain milling is its ability to utilize multiple cutting edges during the operation, which can result in smoother surface finishes. This capability often leads to higher quality outcomes compared to plain milling, which may require additional finishing processes to achieve the same level of surface quality. As a result, when precision surface finish is a critical requirement, contour milling may be the preferred choice.
The choice between plain milling and other milling processes often depends on design requirements and the desired outcomes. Plain milling tends to be more straightforward, involving simpler setups and operations. Conversely, contour milling may involve more complex configurations and toolpath programming, necessitating greater precision and planning. This complexity can be beneficial for producing intricate designs but may require more time and expertise to execute.
In summary, while plain milling is effective for basic applications focusing on flat surfaces, other milling processes like contour milling offer greater versatility and precision for complex geometries and higher surface quality, making them suitable for a wider range of design requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plain milling is a vital machining process that provides high precision and efficiency in creating flat surfaces and features on various materials. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make it an invaluable method in modern manufacturing. By understanding the process, tools, advantages, and applications of plain milling, manufacturers can optimize their operations and achieve superior results. Whether you’re an experienced machinist or just starting, mastering plain milling can significantly enhance your production capabilities.
Final Thoughts
As a professional with 15 years of CNC machining service experience, I can attest to the effectiveness of plain milling in various applications. For instance, at Ultirapid, we’ve successfully utilized plain milling to produce precision components for aerospace clients. In one project, we achieved exceptional surface finishes on engine housings, enhancing their performance and reliability. The simplicity and efficiency of plain milling allowed us to meet stringent deadlines while maintaining quality standards. I highly recommend considering plain milling for your projects, and at Ultirapid, we’re equipped to deliver top-notch machining solutions tailored to your needs. Our expertise ensures that your components will meet the highest industry standards.
Faqs
Is Choosing The Right Plain Milling Cutter Important?
Selecting the right plain milling cutter is crucial for achieving optimal results. The cutter’s geometry, material, and size can significantly impact the machining process, including material removal rate, surface finish, and tool life. A well-chosen cutter helps minimize issues like vibration and tool wear, ensuring efficiency and precision in your operations.
Is Plain Milling Expensive?
The cost of plain milling can vary based on factors like material, tool selection, machine setup, and operational overhead. Generally, plain milling is considered cost-effective due to its simplicity and efficiency. When compared to more complex machining processes, it often requires less time and fewer specialized tools, making it an economical choice for producing flat surfaces and features.
What Are The Common Tools For Surface Milling?
Common tools for surface milling include:
Flat End Mills: Ideal for creating flat surfaces and grooves.
Face Mills: Designed to cut flat surfaces while providing a better finish.
Slab Mills: Suitable for removing large amounts of material quickly.
Keyway Cutters: Specifically used for cutting keyways and slots in various components.
What Is The Processing Speed And Efficiency Of Surface Milling?
The processing speed and efficiency of surface milling depend on several factors, including material type, cutter speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. Generally, plain milling can achieve high material removal rates, particularly when optimized cutting parameters are used. Efficient setups can significantly reduce cycle times, enhancing productivity while maintaining the required tolerances and surface quality.